
Medications used to treat eczema
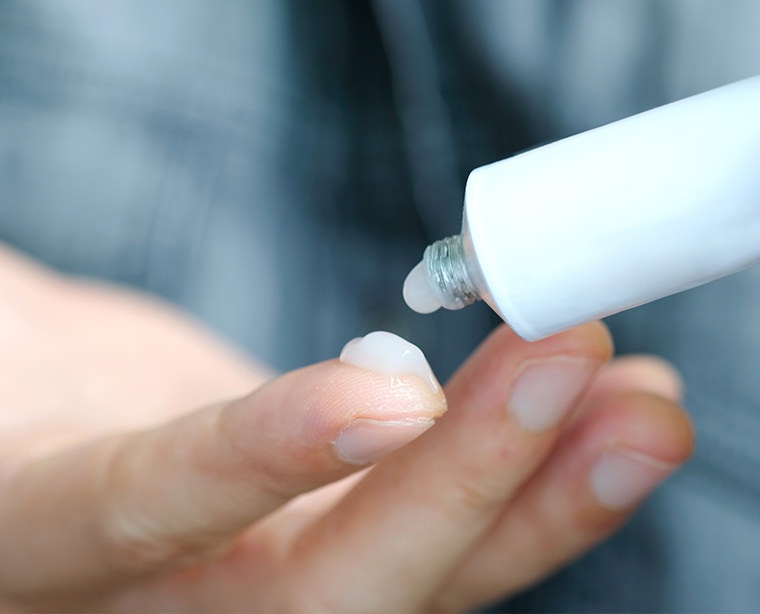

Whether you have atopic eczema or contact eczema, corticoid cream can help soothe inflammation.
For atopic eczema, cream-based anti-inflammatories are used in combination with regular skin hydration. Other treatments may be used, particularly for more severe cases.
Dermocorticoids
It is the standard medication used to soothe redness and thus prevent scratching.
Dermocorticoids are anti-inflammatories: they reduce inflammation, almost like a fire extinguisher puts out a flame.
In the case of atopic eczema, dermocorticoids are only half the treatment. They are combined with a preventive hydrating treatment to promote skin repair. Good hygiene practices and a consistent treatment is the best way to delay the onset of the next flare-up.
Dermocorticoids may be applied to the skin in other forms besides a cream, including ointments, gels, lotions, etc.
Other treatments and medications
In the case of contact eczema, treatment involves avoiding contact with the triggering allergen. Additional treatments are sometimes used: oral corticosteroids for very acute forms, retinoids for severe chronic hand eczema, etc.
When atopic eczema appears on sensitive areas, like on the face or eyelids, another anti-inflammatory, such as an immunosuppressant, may be applied in place of corticoid cream.
Aside from topical treatments, phototherapy, immunosuppressants, or targeted biotherapies are among other treatments reserved for severe forms of atopic eczema.

