Eczema in adults: everything you need to know
Although other types of eczema exist, atopic eczema and contact eczema are the most common.
Atopic eczema in adults
Atopic eczema is also known as atopic dermatitis.
Atopic eczema symptoms
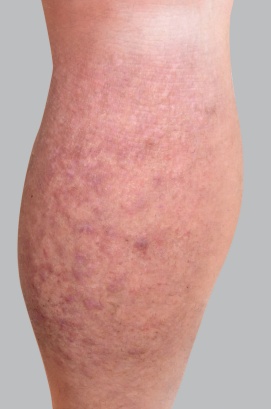
- Dry or very dry skin: Atopic dermatitis is accompanied by varying degrees of skin dryness, which is widespread and permanent.
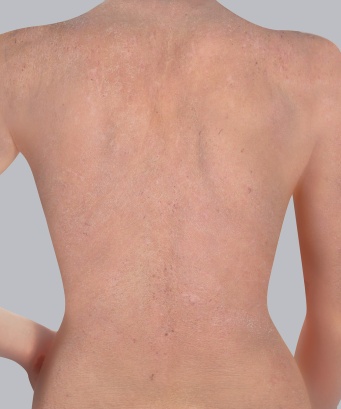
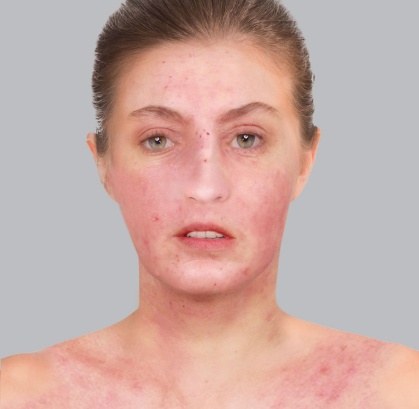
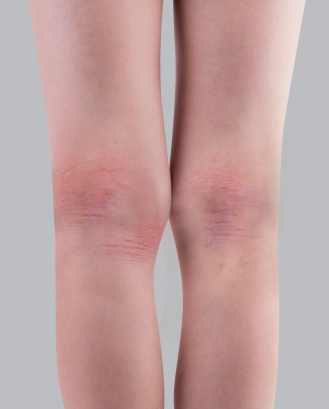
- Red patches: During a flare-up of atopic dermatitis in adults, red patches can appear on the face, neck, and hands, as well as on the inside of the elbows and the back of the knees. This is often the first visible symptom of the flare-up.
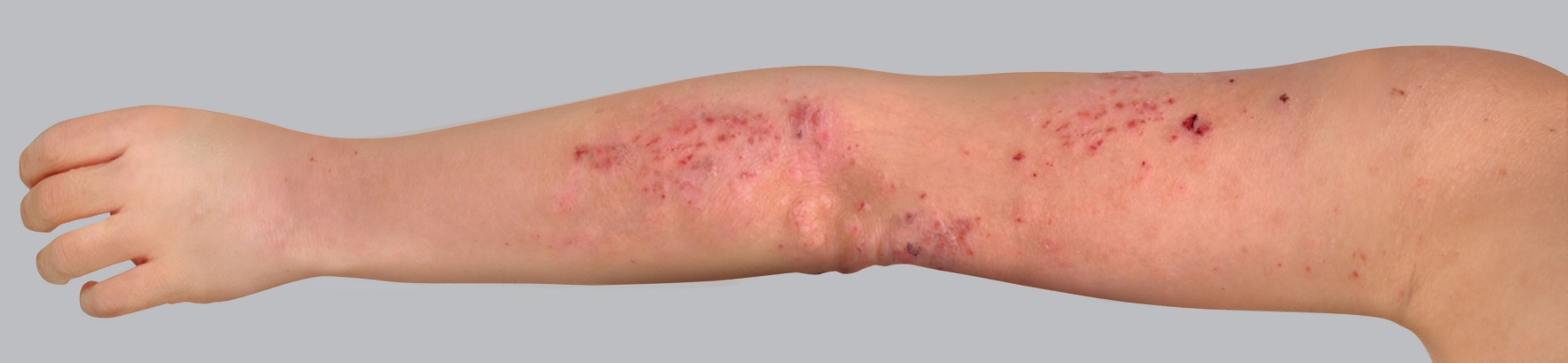
- Weeping: The appearance of vesicles on the patches contributes to itching crises. These can burst and lead to weeping before turning into crusts or scales when they dry out.
- Skin thickening: Due to intense scratching and recurrent patches in the same area, the skin can thicken, visible by an accentuation of the normal skin lines. This is referred to as lichenification, which is maintained by scratching.
- Itching (referred to as pruritus by specialists): An eczema flare-up in adults is always accompanied by significant itching. This can lead to major sleep disturbances and high irritability.
- Scratch marks: Any itching leads to scratching that damages the skin. Where the epidermis is torn, scratching leaves marks, called excoriations.
The severity of symptoms can vary from one adult to another.
In most cases, atopic eczema goes away before the adolescent and adult years, but some patients continue to experience symptoms later in life. Atopic dermatitis in adults can be a serious dermatosis, manifesting as chronic, thick, lichenified red patches. In cases of chronic eczema, patients experience vesicular or oozing flare-ups which alternate between periods of remission.
Itching is always intense and affects patients’ daily lives, mood, sleep and activities.
Where on the body are the patches located?
The hands, face and especially the eyelids are very often affected in adults. In some cases, however, patches appear in large skin folds and other areas of the body.
Face, arms, stomach, legs...
Inflammatory flare-ups can affect the entire skin surface (erythroderma). These widespread episodes are serious, possibly leading to complications such as infections and metabolic disorders, and require hospitalization.
A particular case: "head and neck" dermatitis
A particular form of atopic eczema in adults appears exclusively, or predominantly, on the face and neck. Here, we look for a potential abnormal sensitivity to the sun (photosensitization) which may be caused by, among other things, a secondary yeast infection.
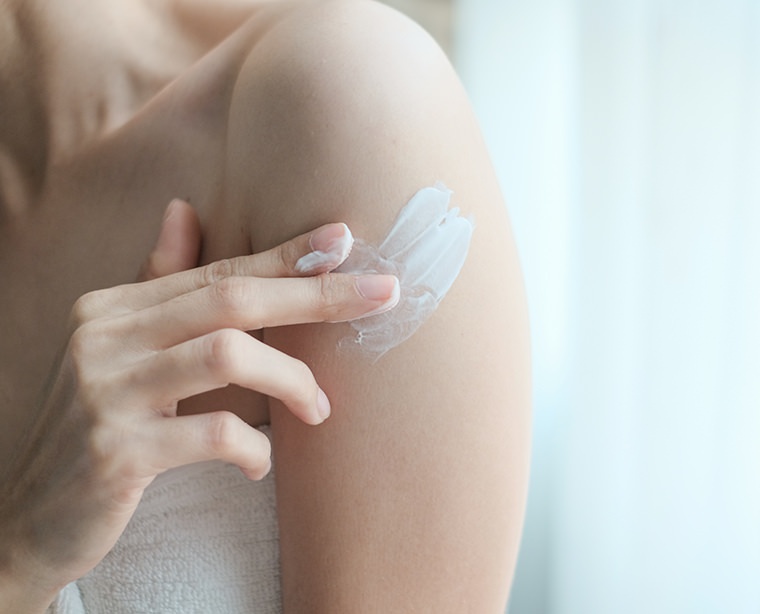
Treatments for atopic eczema are usually combined with an anti-inflammation corticosteroid treatment (known as “topical corticosteroids”) to calm flare-ups, and with an emollient which is critical for hydrating and thus repairing the skin.
Atopic skin is especially sensitive, and seemingly ordinary stimuli can trigger eczema flare-ups. It is helpful to know about the good habits to adopt in terms of cosmetics, diet and more. Various tools are available to lead a more peaceful professional and social life on a daily basis and to eliminate stress as an aggravating factor.
The causes of atopic eczema
Atopic eczema is a hereditary disease linked to a malfunction in the skin (which becomes more porous to irritants and allergens) and in the immune system (which becomes hyperactive). Skin becomes irritated and inflamed in response to various factors, including heat, scratching, stress, and overly harsh cleansers.
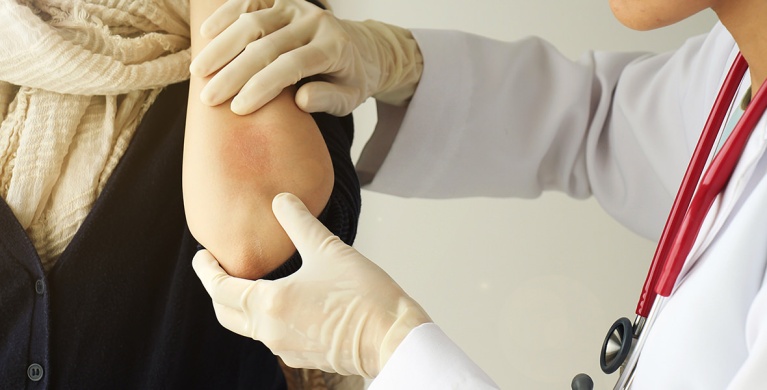
Is atopic dermatitis common?
Atopic dermatitis generally disappears during adolescence, with less than 10% of cases persisting into adulthood. These persistent eczemas should be managed by a specialist, so that appropriate treatment can be considered, if necessary, in addition to the application of a cortisone cream and an emollient.
Does eczema go away on its own?
Atopic eczema evolves over the course of an individual's life and disappears on its own in the majority of cases in adolescence. But the "atopic terrain" is always there. An emollient can remain useful for rebuilding the skin barrier and compensating for skin dryness.
It is rare for a flare-up to disappear on its own; a dermocorticoids cream must be applied for a few days to reduce inflammation and soothe the flare-up.
Contact eczema in adults
An allergic reaction
In the case of contact eczema, skin experiences inflammation after coming into contact with an allergen. A reaction to costume jewelry is the classic example.
The main causes of allergic contact eczema
- Nickel found mainly in metals used to make costume jewelry, glasses frames and mobile phones
- Preservatives and other ingredients in cosmetics, fragrances, cleansers or sun care products
- Even fragrances and essential oils in so-called “organic” cosmetics (no hypoallergenic guarantee)
- Components of clothing and footwear (chromium in leather, adhesives).
Some products or objects commonly used in certain professions can cause contact eczema. Adhesives, dyes, gloves, industrial oils... the list is endless!
Solutions and treatments
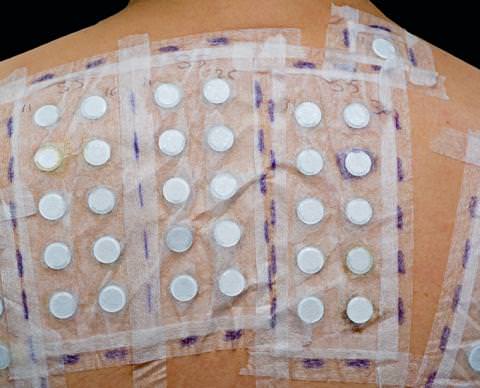
Topical corticosteroids are highly effective at treating eczema. To prevent recurrence when a contact allergy is suspected, allergy tests are required to identify the substance responsible for the allergic contact eczema and to learn how to avoid it in the future. A simple interview may be enough to pin down the cause and to eliminate it from your daily life in order to ensure treatment.